User interface and user experience design are two important concepts in the world of web and app design. Both elements are crucial to a product and work closely together.
But despite their professional relationship, the roles themselves are quite different, referring to very different aspects of the product development process and the design discipline.
What are UI and UX Design?
UX design refers to “user experience design,” while UI stands for “user interface design”. UI Design focuses on a product's visual design, while UX Design focuses on the user experience. The truth is UX and UI are two sides of the same coin.
Think of it this way: UX is about how a product feels. UI is about how a product looks.
Before considering the key differences between UX and UI, let’s first define what each term means individually.
What is User Interface(UI) Design?
UI design is the process of making interfaces in software or computerized devices with a focus on looks or style. Designers aim to create designs users will find easy to use and pleasurable.
The term was coined by Joel Spolsky in 1995 when he launched the first discussion forum for UI designers, calling it the “User Interface Design Group”.
UI design, at its core, is focused on the user interface — anything that a user interacts with. This encompasses everything from buttons and icons to drop-down menus and sliders to text fields and images.
The goal of user interface design is to make the user’s interaction as simple and efficient as possible.
Why is User Interface Design important?
“If a website was a house, then the visual design would be interior decorating.”
User interface design is important because it can make or break your customer base. It can be the difference between a successful app or website and one that fails. It can also mean the difference between customers staying on your site or leaving it.
An effective UI design can also make your product more visually appealing, which can help you capture the attention of potential customers. In addition, a well-designed UI can help you build a strong brand identity for your product.
If you want your product to stick out in the marketplace, then investing in a good UI design is a must.
In a nutshell, this is what user interface (UI) design is all about:
User interface design is a purely digital practice. It considers all the visual and interactive elements of a product interface—including buttons, icons, spacing, typography, color schemes, and responsive design.
The goal of UI design is to visually guide the user through a product’s interface. It’s all about creating an intuitive experience that doesn’t require the user to think too much!
UI design transfers the brand’s strengths and visual assets to a product’s interface, making sure the design is consistent, coherent, and aesthetically pleasing.
It’s crucial to have a beautiful and consistent UI to create an enjoyable user experience (UX). But what is UX design? Let’s understand.
What is User Experience(UX) design?
“A website with a beautiful interface but poor performance is like a Lamborghini with a Toyota engine.”
UX design is more than just a buzzword. It’s the difference between a website that people like to visit and one they can’t wait to leave.
UX designers are tasked with shaping the overall user experience of a website or web application, focusing on how it feels, functions, and looks.
In other words, good UX design is all about making sure that a visitor to your site has a good experience when they’re there.
Why is user experience design important?
In the case of a website, UX design includes everything from aesthetics to whether or not a site is usable, and it plays a vital role in your company’s success. Customers who have positive experiences are likely to return, while those who don’t can form negative opinions of your brand that they’ll share with others.
In the case of a product, UX designers are responsible for the user experience (UX) of the product. Their job is to ensure that the product logically flows from one step to the next. UX designers solve for usability first and aesthetics second.
A UX designer thinks about how the experience makes the user feel and how easy it is for the user to accomplish their desired tasks. They also observe and conduct task analyses to see how users complete tasks in a user flow.
For example, how easy is the checkout process when shopping online? How easy is it for you to grip that vegetable peeler? Does your online banking app make it easy for you to manage your money?
The ultimate purpose of UX design is to create easy, efficient, relevant, and all-around pleasant experiences for the user.
Overall, this is what user experience(UX) design entails:
User experience design is the process of developing and improving the quality of interaction between a user and all facets of a company.
User experience design is, in theory, a non-digital (cognitive science) practice but is used and defined predominantly by digital industries.
UX design is not about visuals; it focuses on the overall feel of the experience.
UI vs. UX Design: The Difference Between the Two
It’s like asking, “What is the difference between red paint and the chemicals the paint is made up of?” There is no difference. Red paint is made up of all sorts of different chemicals that, when combined, make red paint.
Just as the user experience is made up of a bunch of different components, with user interface design being just one of them, when combined makes up the user experience.
If we’re talking about delicious cake, UI is the icing, the plates, the flavor, the utensils, and the presentation. UX is the reason we’re serving cake in the first place, and why people would rather eat it than hamburgers.
UI design and UX design go hand-in-hand; you can’t have one without the other.
But don’t worry if you’re still confused! You’re not the only one!
If you’ve got room for one more analogy, Dain Miller sums up the relationship between UX and UI design perfectly:
“UI is the saddle, the stirrups, and the reins. UX is the feeling you get being able to ride the horse.”
—Dain Miller, Web Developer
It’s important to understand that UX and UI do go hand-in-hand; you can’t have one without the other. However, you don’t need to possess UI design skills to be a UX designer, and vice versa—UX and UI constitute separate roles with separate processes and tasks!
User interface (UI) design is about making the product look good. It’s about adding colors, borders, icons, shadows, and all sorts of other visual flairs. It’s also about making sure that those elements fit into a larger whole that makes sense from both a visual and functional perspective.
User experience (UX) design is the process of systematically improving a product so that it is more intuitive, efficient, and user-friendly. Doing so involves considering how different parts of the product interact with each other, and how they’re perceived by users.
So when you think of UI vs UX design, just remember that your user interface is only one part of the equation.
From the perspective of a user, there is no difference. The experience is what you feel and think when you interact with a product or service.
From the perspective of a designer, there is a big difference. They are two completely different fields of study. While they share some common interests, they don’t overlap.
Both elements are crucial to a product and work closely together. But despite their professional relationship, the roles themselves are quite different.
So what's the difference?
UI designers focus on making things look good. They’re concerned with aesthetics and creating a product that has a consistent style and looks that appeal to users. A UI designer will work closely with a UX designer to make sure that their designs fit in with the requirements of the UX designer.
UX designers focus on making sure that a product is easy for people to use. They’re concerned with optimizing the flow of information—how easy it is for users to get from point A to point B, for example. They also ensure that products are engaging so that users want to keep using them.
UX design is the process of building a website (or app) that is both functional and intuitively easy to use. It focuses on the “satisfaction” aspect of a user’s experience.
UI design, on the other hand, focuses on making sure each screen looks its best visually and serves its purpose in an overall product.
In summary:
UX design is all about identifying and solving user problems; UI design is all about creating intuitive, aesthetically-pleasing, interactive interfaces.
UX design usually comes first in the product development process, followed by UI. The UX designer maps out the bare bones of the user journey; the UI designer then fills it in with visual and interactive elements.
UX can apply to any kind of product, service, or experience; UI is specific to digital products and experiences.
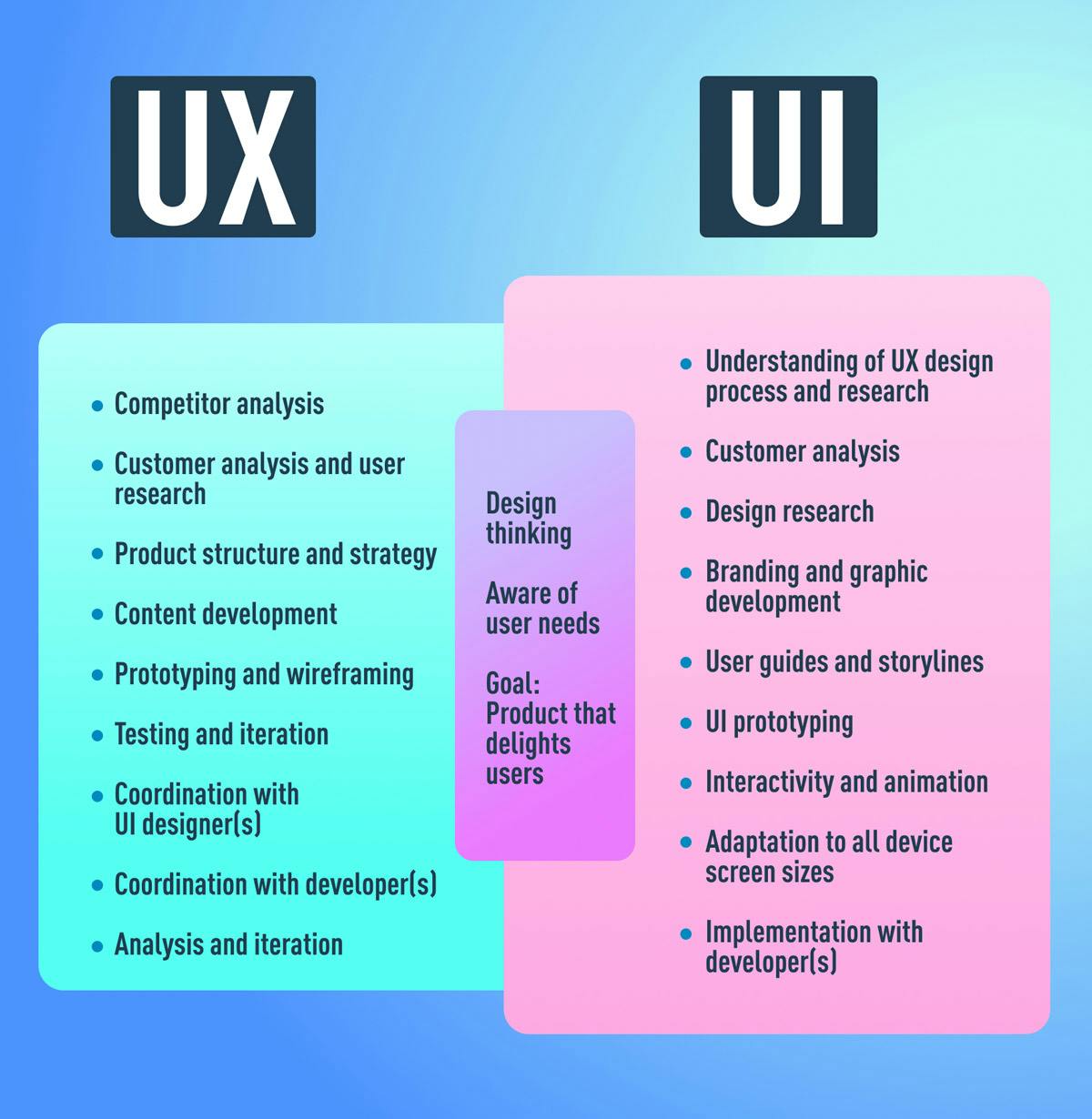
Conclusion
UI and UX work together but are different. UX design is more analytical. It’s rooted in cognitive behavior and human psychology. UI design software is focused more on the visuals—or whether a product is aesthetically pleasing.
The UX design process is the framework or strategy that guides how a designer or team of designers tackles a project. It’s the series of steps or actions a designer takes to best solve a problem for their user.
Some examples of this would be conducting user research, creating wireframes and prototypes, testing, iteration, and presentation.
The UI process is the set of steps and actions that are taken to turn UX design into reality. The UI process revolves around the definition of style and brand guidelines that must be followed to create a cohesive experience between all your products.
Some examples of this would be defining color palettes and typography, creating basic elements such as buttons and icons, designing page layouts and templates, and developing style guides.
UX has more to do with the actual functionality and content of a website or app, while UI is the look and feel and how people interact with it.

